Integrated modular platform
State of the art of digital platforms for cultural site management
The work focused on a careful review of the state of the art regarding approaches in the scholarly literature related to the semantic enrichment of a BIM environment in the Heritage domain using external databases and "Internet of Things" IoT resources. The analysis consisted of two phases: a first phase, in which significant contributions were identified by drawing in literature reviews and performing a keyword search in academic databases, journals, and conference proceedings. The main keywords were HBIM, architectural heritage, database, semantic enrichment, IoT, digital Twin. The second stage of the critical analysis allowed us to restrict the review to only those papers that were clearly oriented toward enrichment of current BIM tools through databases and external resources in the field of architectural heritage and therefore met all or part of the following requirements: use the BIM tools available today, have case studies related to architectural heritage, make use of external databases and/or IoT resources. In a nutshell, the work done showed that, in several cases, there are multiple points of contact and overlap between one or more aspects of the workflows. In fact, all the work shares the use of external databases to establish the link between the BIM environment and specific external resources used to enrich the semantic layer of the representation. More specifically, there is a rapid increase in "vertical" applications of the digital twin to the built heritage, to be understood as cyber-physical systems designed and implemented to control specific critical aspects of that domain, such as monitoring the state of decay or controlling the environmental conditions of the same, also with a view to energy sustainability during the building's operation.
Having concluded the collection of articles, a summary paper was prepared to illustrate in more detail the evolution of research in the domain of interest and especially what technological-implementative solutions have been identified to be able to extend the domain of representation of BIM tools on case studies concerning historic buildings using sensors.
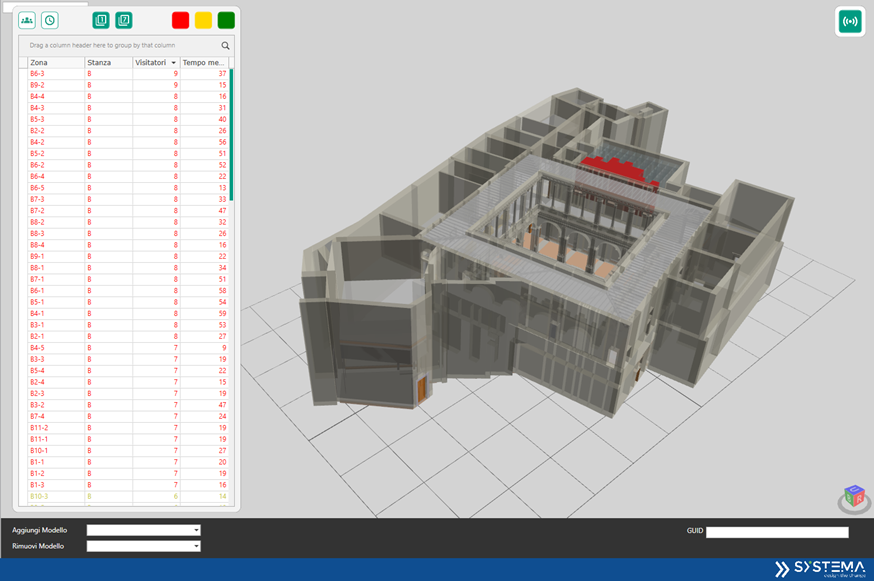
Development of the integrated modular platform
The preliminary architecture of the HBIM-IoT platform, i.e., the information enrichment system that integrates the data flow produced by the sensor components for user monitoring with the BIM model of a museum structure, was defined as a system according to its purpose and with a view to agile system management that does not require specific BIM modelling skills.
The platform consists of:
- A BIM software environment for graphical presentation and model manipulation in the context of the user interface, usable via a browser;
- An IoT part that allows both to simulate virtual sensors and to interface with physical IoT elements.
A crucial theme is that of visualizing the results of diagnostic monitoring surveys with IoT sensors, to be linked to the three-dimensional geometric and informational model of the building. The solution considered to be most adoptable in technical terms involved an extension of the selected platform so that a user can access the system through a Web interface. This interface allows both the function of aiding the 'visual' navigation of the extended model and as a dashboard dashboard for the function of representing the monitoring indices.
The possibility of dynamic exchange with other databases and systems in terms of the interoperability of the HBIM process ensures that information is constantly updated. To this end, synergies are active with the IDEHA project, coordinated by ISPC-CNR, where send-and-return data flow between HBIM model and IoT for environmental monitoring is being tested.
The system is designed in order to ensure, on the one hand, a fruition for a competent BIM user and therefore interested in 3D modeling, visualization and 3D/informative consultation of the model in modes typical of these processes; on the other hand, the possibility of a simplified fruition of diagnostic data on the web similar to traditional management processes is provided.
The activity of defining the application methodology of the platform on the demonstrator cases was conducted in consultation with the managing body of the museum concerned the definition of solutions that take into account the current organizational structure of the museum.

